4 Reasons to Visit a Hearing Health Professional
Hearing health is something that should be taken seriously. If you are
Your Best Hearing, Your Best Life.
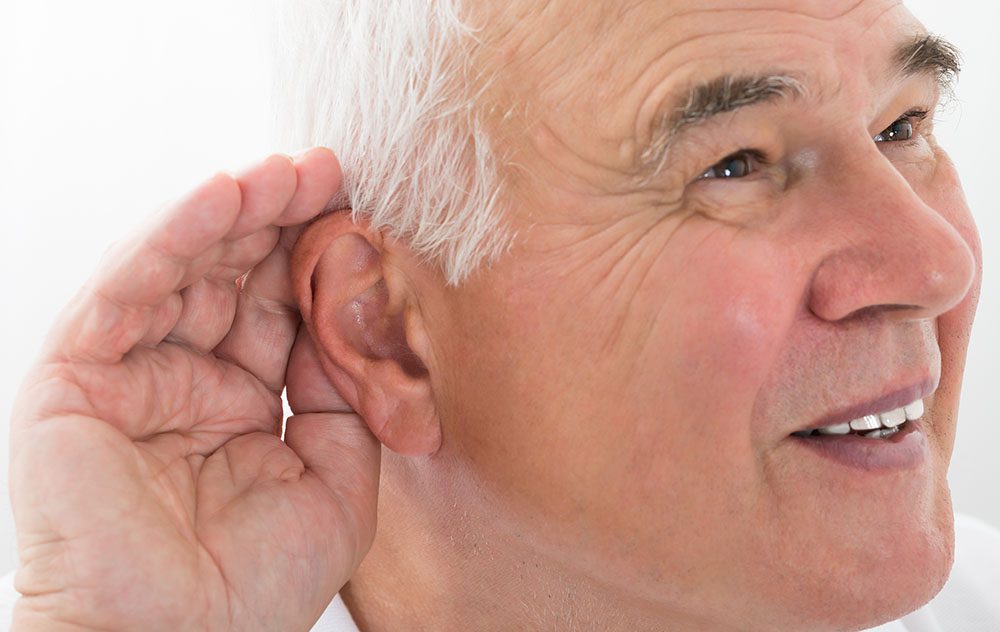

Hearing health is something that should be taken seriously. If you are

An audiologist plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal hearing health,

Earwax is a substance that everybody has and produces but is not a topic